SCAN Disk Scheduling
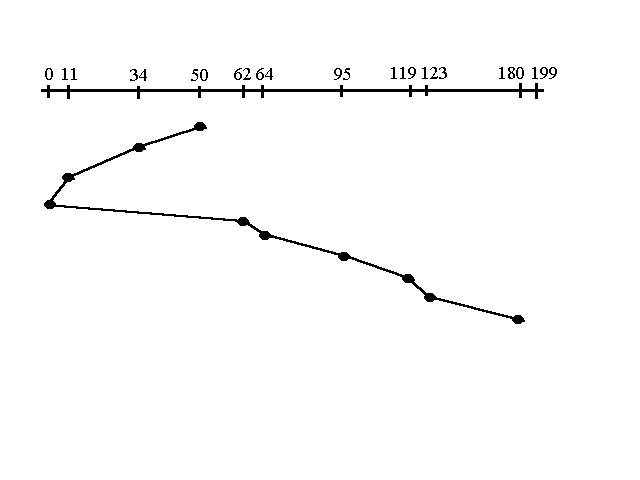
This approach works like an elevator does. It scans down towards the nearest end and then when it hits the bottom it scans up servicing the requests that it didn't get going down. If a request comes in after it has been scanned it will not be serviced until the process comes back down or moves back up. This process moved a total of 230 tracks. Once again this is more optimal than the previous algorithm, but it is not the best.
AdvantagesDisadvantages
EXAMPLE : Lets say we are given with the following queue ==> 95, 180, 34, 119, 11, 123, 62, 64 with the Read-write head initially at the track 50 and the tail track being at 199 let us now discuss the different algorithms.